
13 Feb What is HTTPS? And why you need it for the new Google update
Why do I want HTTPS?
Google, and other browsers, have gradually started to encourage their users to look out for sites that don’t use ‘HTTPS’ or sometimes call an SSL certificate.
Does your site collect sensitive visitor information such as passwords, credit card information, or personal data? Google has announced a deadline of July 2018as the date for when Chrome will begin explicitly warning users if a site is insecure. Over 50% of Internet browsers worldwide are Chrome,
The word from Google is that they have already started to rank sites WITH SSL higher than sites without SSL. This article shows Google talking about HTTPS as a method for ranking websites.
Reasons to get SSL:
- Better ranking in Google, and
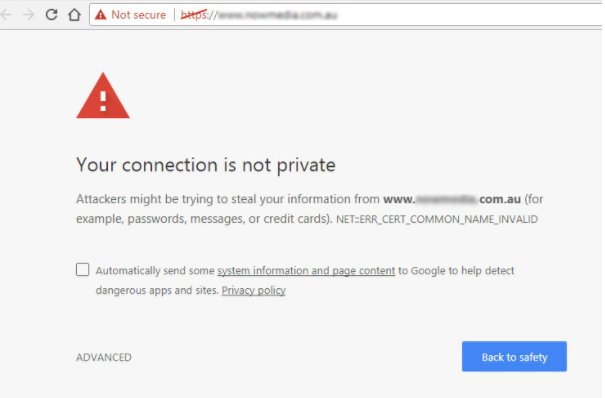
- Visitors who feel secure on your site. (Otherwise they may get a message: ‘Not secure” as below)
You may have noticed that if a site is secure, you get a little green padlock in the address bar:

HTTPS, can’t solve every problem when it comes to online security. As far as preventative measures go, however, it’s relatively cheap to implement and serves as a strong baseline before tackling other, more difficult issues.
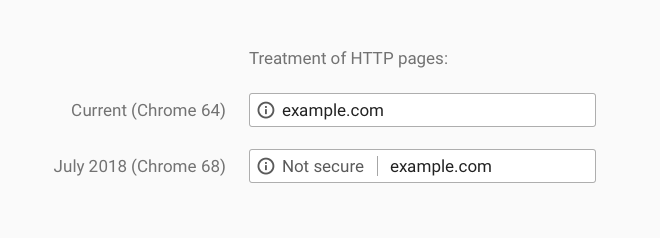
That’s why, starting in July 2018, Google will start labelling all sites still using unencrypted HTTP as “not secure” on version 48 of Chrome. This sort of tagging will inform users about how sites they visit operate, while also putting a bigger burden on websites owners to switch over.
Right now, Google says, 68 per cent of Chrome traffic on Android and Windows is protected, while that number rises to 78 per cent on Chrome OS and Mac, with 81 of the top 100 sites on the web using HTTPS by default.
Without an SSL, website owners may not be viewed as ‘legitimate’ to new customers searching them online.
Existing customers may not be able to make a purchase either, as eCommerce payment gateways are stopping all payments going through non-secure sites.
“Enabling HTTPS on your whole site is important, but if your site collects passwords, payment info, or any other personal information, it’s critical to use HTTPS.”
What is SSL?
SSL stands for Secure Socket Layer and is sometimes used interchangeably with the term TLS – Transport Layer Security. It’s just a fancy cryptographic protocol that helps encrypt communications over a computer network.
What Is HTTPS?
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. It’s used to transmit secure communications over a computer network, like the internet. It helps keep your data safe so no one tampers with it and to make sure it isn’t forged. (HTTP is the non-secure version of HTTPS.) (This will happen when the SSL is applied to your site)
What is the change?
The three reasons Google has for securing your website are:
Authentication verifies the ownership of your website, because there are people out there who will make replicas of your website in an effort to steal from you. (Most people know to check for the green lock in the address bar before handing over their personal details.)
Data integrity means whether or not the data has been tampered with when it’s in transit. If someone knows your website isn’t secure, they can tamper with the data being transmitted.
Encryption is the security of the communications between the client and the server to make sure no one else can read them. It’s important to encrypt the data in forms, as well as credit card information for ecommerce sites.
How can I check my site?
1. 
2. 
3. 
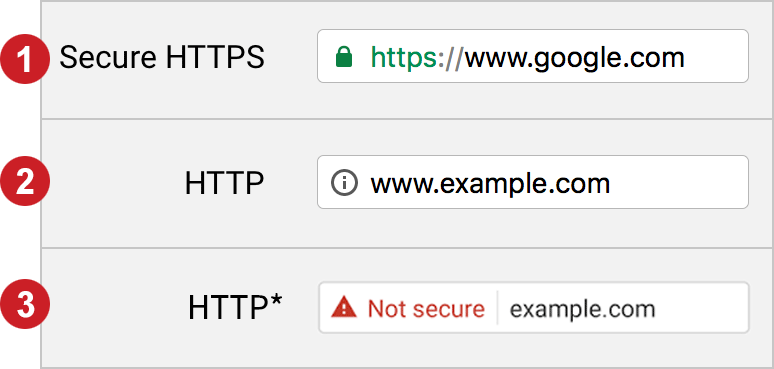
Image credit: Netregistry
How do I get HTTPS?
Easy! Contact us today and we will get your site secure and make sure you are not effected by Googles new changes.
If you don’t have an SSL certificate on your website, you run a massive risk of losing valuable business – especially for those who rely on their website traffic for direct leads and sales.



















